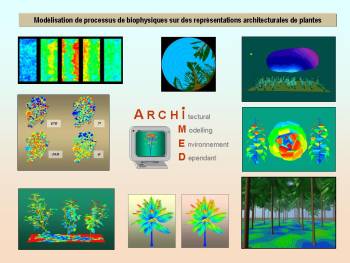
Archimed
Most classic ecophysiological models rely on crude representations of canopies as stacks of vegetation layers. Therefore, their use in complex canopies implies complicated adaptations as well as simplifying assumptions that are difficult to validate.
Alternatively, the ARCHIMED simulation platform uses 3D virtual stands as a support for numerical simulations of biophysical processes such as leaf irradiation, transpiration and temperature and ultimately carbon assimilation. By doing so, detailed information can be integrated from the individual leaf scale up to the individual plant scale, even within complex stands such as agroforestry systems. Simple numerical methods are used for solving multiple feedbacks between light, energy, water and CO2 transfers at leaf, plant and plot scales. Numerical calculations applied at different scales allow simple implementation of complex models involving intricate processes.
The modules implemented in AMAPstudio are:
- MMR for calculating the radiative balance of items within a 3D scene (MMR)
- ART for simulating Lidar bascattering (ART)
- TreeShape, a utility for designing simple tree shapes
- see also VPalm
Dauzat, J., Franck, N., Rapidel, D., Luquet, D., Vaast, P., 2006. Simulation of ecophysiological processes on 3D virtual stands with the ARCHIMED simulation platform. PMA06: The Second International Symposium on Plant Growth Modeling, Simulation, Visualization and Applications. Beijing, P. R. China : PMA06: The Second International Symposium on Plant Growth Modeling, Simulation, Visualization and Applications, 13-17 November 2006, Beijing, P. R. China.